



Next: Resonances
Up: Ring-resonator theory
Previous: ``Standard model'' for resonators:
Contents
Due to the linearity and the symmetry of the device, it is sufficient to
consider an excitation in only one of the external ports, say port 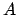 . Given
input amplitudes
. Given
input amplitudes
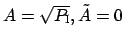 , one is interested in
the transmitted power
, one is interested in
the transmitted power
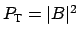 and the dropped power
and the dropped power
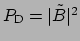 . By solving equations (1.1) and
(1.2) for amplitudes
. By solving equations (1.1) and
(1.2) for amplitudes 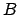 and
and 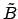 , one obtains
, one obtains
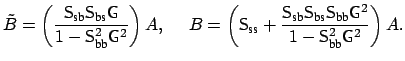 |
(1.3) |
Let
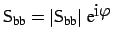 ,
,
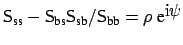 with
with 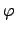 ,
, 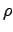 and
and 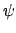 real. Then the dropped power is
given by
real. Then the dropped power is
given by
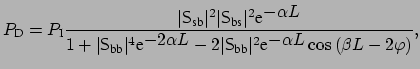 |
(1.4) |
and the through power is given by
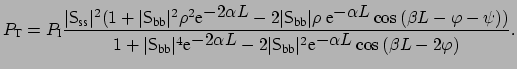 |
(1.5) |
Here 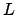 is the total length of those parts of the cavity which are not already
included in the couplers. According to equations (1.4) and
(1.5), one can evaluate the throughput power and the dropped
power, if the scattering matrix
S and the cavity propagation constant
is the total length of those parts of the cavity which are not already
included in the couplers. According to equations (1.4) and
(1.5), one can evaluate the throughput power and the dropped
power, if the scattering matrix
S and the cavity propagation constant
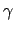 are available.
are available.




Next: Resonances
Up: Ring-resonator theory
Previous: ``Standard model'' for resonators:
Contents
Kirankumar Hiremath
2005-09-23
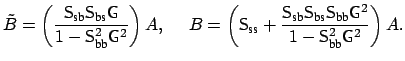
![]() ,
,
![]() with
with ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() real. Then the dropped power is
given by
real. Then the dropped power is
given by